Hearing aids, small yet life-changing devices, are designed to amplify sounds and improve the hearing abilities of those with hearing loss. These devices typically consist of a microphone to capture sounds from the environment, an amplifier to increase 弱聽治療 volume of those sounds, and a speaker to deliver the amplified sounds into the ear canal. Modern hearing aids go beyond merely making sounds louder; they also enhance the quality of sound by filtering out background noise and focusing on speech. This significant advancement has made hearing aids essential tools for millions of people worldwide, helping them to engage in meaningful conversations, enjoy social activities, and improve their overall quality of life.
The history of hearing aids is a fascinating journey of technological evolution. From simple ear trumpets used in the 17th century to today’s digital devices, hearing aids have undergone significant transformations. Early models were bulky and relied on basic acoustic amplification, offering limited benefits. However, the development of the transistor in the 1950s marked the beginning of more portable and efficient devices. With the advent of digital technology in the 1980s, hearing aids began to incorporate signal processing features, allowing for more precise adjustments to match individual hearing loss profiles. Today’s hearing aids use cutting-edge digital algorithms to adapt to different listening environments automatically, providing a seamless auditory experience.
The primary function of a hearing aid is to improve communication by amplifying sounds, but it also serves to enhance safety and awareness. For individuals with hearing loss, everyday situations such as crossing a street, hearing a fire alarm, or following conversations in noisy places can be challenging and even dangerous. Hearing aids help to restore some level of natural hearing, making it easier for users to detect warning sounds and respond accordingly. The devices are also beneficial in educational and professional settings, where effective communication is critical. By enabling users to hear more clearly, hearing aids can positively impact job performance, social relationships, and overall well-being.
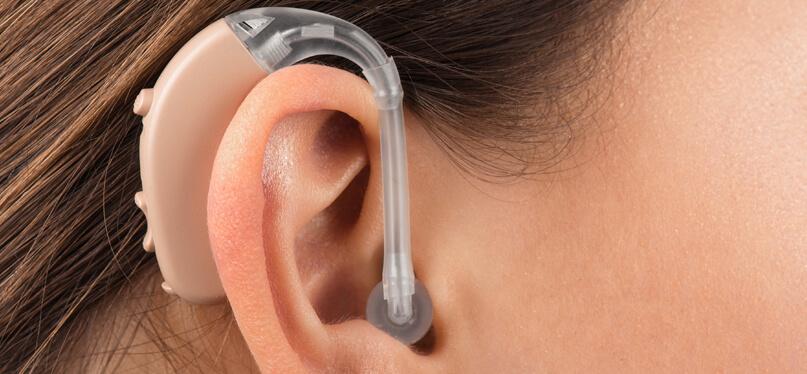
Today’s hearing aids come in various styles and configurations, each designed to cater to different types of hearing loss, lifestyle preferences, and cosmetic considerations. The most common types include behind-the-ear (BTE) models, which consist of a small case placed behind the ear and a tube connecting to an ear mold inside the ear canal. In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids are custom-made to fit the outer ear, making them more discreet, while in-the-canal (ITC) and completely-in-canal (CIC) models are even smaller, sitting deeper inside the ear. Each style has its own set of advantages, with BTEs typically offering more power and features, while CICs provide greater cosmetic appeal for those seeking a nearly invisible device.
Hearing aids are not just limited to traditional hearing loss solutions; they also feature advanced technologies that improve user experience. Bluetooth connectivity is a common feature, allowing users to stream audio directly from their smartphones, televisions, or other compatible devices. Some hearing aids even come with telecoil technology, which enables better listening in places equipped with induction loop systems, such as theaters or places of worship. Modern hearing aids often include rechargeable batteries, eliminating the need for regular battery replacements, and many are water-resistant, providing additional durability and convenience for users.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly playing a role in the development of next-generation hearing aids. AI-powered hearing aids can learn the user’s preferences and automatically adjust settings to optimize sound quality in different environments. For instance, they can differentiate between background noise and speech, providing better clarity during conversations. Some AI-enhanced models are capable of detecting falls or monitoring vital signs, offering health-tracking features that go beyond hearing. These intelligent devices represent a shift towards a holistic approach to hearing health, integrating technology that supports overall well-being.
Despite the advancements in hearing aid technology, there are still challenges to widespread adoption, particularly due to cost and accessibility. Hearing aids can be expensive, often ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per device, and they are not always covered by insurance plans. This financial barrier can prevent some individuals from obtaining the necessary help for their hearing loss. Additionally, the stigma associated with wearing hearing aids can discourage people from seeking treatment, especially younger individuals who may feel self-conscious about using them. Efforts are being made to make hearing aids more accessible and affordable, with some countries offering subsidies or over-the-counter options to reduce costs.
As the global population ages, the demand for hearing aids is expected to rise, with an increasing number of people experiencing age-related hearing loss. Manufacturers are continually innovating to meet this demand by developing hearing aids that are more user-friendly, effective, and cosmetically appealing. The introduction of invisible hearing aids and devices that can be integrated with other wearable technology indicates a future where hearing aids are not only more accepted but also embraced as everyday gadgets. This trend is supported by the growing recognition of the importance of hearing health as a critical component of overall well-being.
In addition to older adults, younger people are also at risk of hearing loss due to noise exposure from loud music, recreational activities, or work environments. This emerging demographic of hearing aid users is driving changes in the design and marketing of these devices. Manufacturers are creating products that appeal to a more tech-savvy audience, incorporating smart features, stylish designs, and even gaming-like interfaces that make the use of hearing aids more engaging. The goal is to normalize hearing aids as modern, desirable accessories rather than medical devices, helping to reduce stigma and encourage early adoption.
Looking ahead, the future of hearing aids is promising, with innovations such as brain-computer interfaces, enhanced sound processing, and greater personalization on the horizon. Research is being conducted to develop hearing aids that can directly interface with the brain, potentially bypassing damaged parts of the auditory system and restoring hearing more effectively. As hearing aids continue to evolve, they will not only enhance auditory experiences but also offer users new ways to interact with their environment, making life more accessible, connected, and fulfilling for those with hearing impairments.